What are oesophageal atresia and tracheo-oesophageal fistula?
Oesophageal atresia (OA) is where the food pipe (oesophagus) does not form correctly and is blocked. Babies with this condition are not able to swallow food or saliva.
Tracheo-oesophageal fistula (TOF) often occurs at the same time as OA. TOF is where a tunnel of tissue called a fistula connects the food pipe to the windpipe (trachea).
When the food pipe and windpipe are connected with a fistula, the contents of the baby’s stomach can travel into the lungs. This can damage the lungs. The stomach can also fill with air which makes breathing difficult.
All babies with OA/TOF need surgery to protect the lungs and allow them to feed. This is successful in most cases, but many children will require further operations during their childhood.
To make sure that we provide the best care possible in Manchester, we review and follow up our children with OA and TOF until they are 16 years old (OA/TOF and CDH clinic).
We have a joint surgical and respiratory clinic so children receive specialist care in one place, reducing the amount of appointments they have to attend and ensuring ‘joined-up’ care.
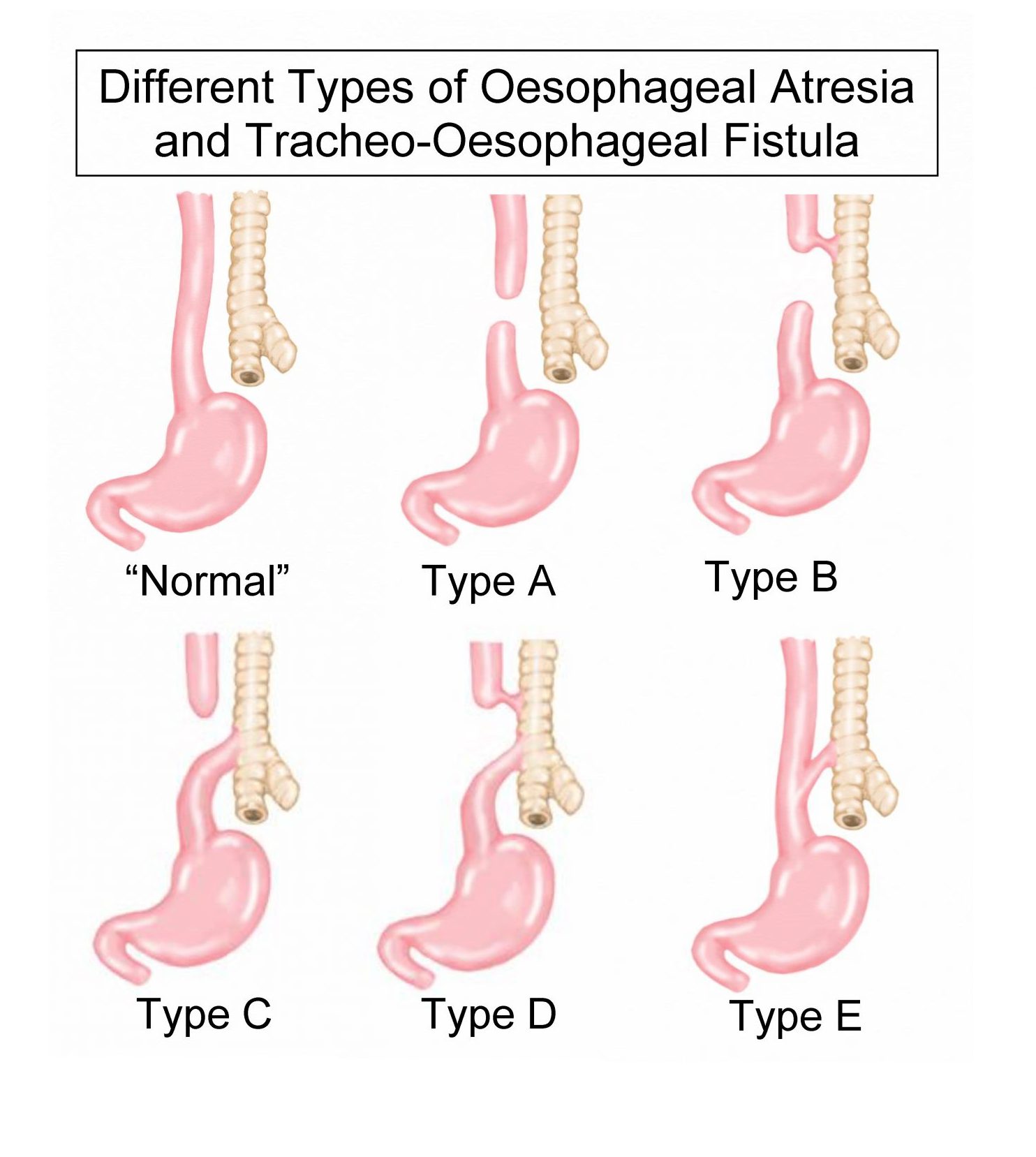
Signs of OA/TOF
During feeding your baby may:
- cough or splutter
- have frothy bubbles coming out of their mouth
Causes
The cause of OA/TOF is not known.
The chance of it developing is the same whether or not a close relative has the condition.
The condition is not caused by anything the parents have done or not done during pregnancy.
The condition is not inherited and any future pregnancy is not at increased risk.
Diagnosis
OA/TOF is sometimes difficult to diagnose.
Your baby may have:
- a soft tube passed up their nose and into their food pipe to feel for a blockage
- a slightly larger and more stiff tube which can be used if the softer tube does not pass into the stomach
- X-rays
- a camera inserted into the windpipe (endoscopy) to look inside for the blockage or fistula
Associated conditions
Polyhydramnious (excess amniotic fluid)
During pregnancy, too much amniotic fluid around your baby in the womb can indicate a health problem. OA/TOF is one of the potential problems but it is not possible to find out for sure until after birth.
Most babies with polyhydramnious will be healthy.
Genetic conditions
Babies with OA/TOF have an increased chance of:
- blockages in the bowel
- conditions affecting the hands, arms, spine, heart, or kidneys
If your baby has OA/TOF they will be tested to check for other conditions. One of the tests will be an ultrasound of their heart, tummy and spine.
Sometimes babies with a syndrome called VACTERL and CHARGE can have OA/TOF.
Treatment
All babies with OA/TOF need urgent surgery to disconnect the TOF (fistula) between the windpipe and food pipe.
This will stop stomach contents from going into the lungs and air going into the stomach.
During the operation it is often possible for the food pipe (oesophagus) to be repaired at the same time, so the baby can then feed. However, in some babies this is not possible and they might need further operations
Surgery
An operation under a general anaesthetic will usually take place in the first day or two of life.
A camera is passed into the baby’s windpipe so the surgeon can look for the TOF (fistula) and any other abnormalities.
The different types of OA require different operations but the principles of the surgery are as follows.
A cut is made in the right armpit and sometimes the cut will extend round towards the back.
- If a TOF is present it will be closed/repaired. This will make it easier for the baby to breathe and protect the lungs from the contents of the stomach.
- If the windpipe is narrow (tracheomalacia), some stitches are sometimes placed at the back of the windpipe to help keep it open. This is called a posterior tracheopexy.
- With OA (blocked food pipe) the blocked section is removed and the two ends joined together.
Sometimes the two ends of the food pipe do not reach each other, so a feeding tube will be put in the stomach. This is called a gastrostomy. It means your baby can feed and grow until another operation to join the two ends of the food pipe together.
Sometimes another part of the bowel will be used to bridge the gap if the distance between the ends is still too large
After the operation
Your baby will be asleep when they return to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
They will be on a ventilator and will have a tube in their mouth going into the windpipe to help them breathe.
Another tube will be in place in their chest to drain fluid and help breathing.
Over the next 2-3 days, the amount of help your baby receives to breathe is slowly reduced.
The breathing tube will be removed when your baby can breathe on their own.
Feeds will initially be given through a tube that passes through their nose into their stomach.
This will usually stay in place for the first week. After this we will encourage most babies to breast or bottle feed.
Complications of OA/ TOF
Gastro-oesophageal reflux
Nearly all babies have some amount of reflux when they are young. Babies with OA/TOF are more likely to have worse reflux that can cause problems. In order to treat this, they will be given a medicine such as omeprazole for at least the first year of life.
A few children will have more significant problems with reflux and will need further treatment such as an operation called a fundoplication.
Oesophageal strictures (narrowing of the food pipe)
The food pipe may become narrow again in some places. This is called a stricture. It can cause your baby to feed more slowly, cough, or choke on milk. If this happens, the food pipe will need to be stretched open in a procedure called dilation.
Dilation for OA/TOF is where a small balloon is passed through the narrow area of the food pipe and then gently blown up to stretch the narrow area open. This is done under general anaesthetic and your baby is usually able to go home the same day.
Further information about OA/TOF
Tracheo-Oesophageal Fistula Support: Homepage
 In this section
In this section